For three decades, Lean Six Sigma (LSS) has helped organizations strip out waste, reduce variation, and build a culture of continuous improvement. Its DMAIC framework remains the de-facto playbook for rooting out hidden costs and reliability issues. The catch? Traditional Six Sigma projects depend on workshops, interviews, detailed time studies, running multiple experiments ‘by hand,’ etc.—manual effort, point-in-time snapshots, and labor-intensive decision-making that can ‘age out’ before the ink on the control chart dries.
For three decades, Lean Six Sigma (LSS) has helped organizations strip out waste, reduce variation, and build a culture of continuous improvement. Its DMAIC framework remains the de-facto playbook for rooting out hidden costs and reliability issues. The catch? Traditional Six Sigma projects depend on workshops, interviews, detailed time studies, running multiple experiments ‘by hand,’ etc.—manual effort, point-in-time snapshots, and labor-intensive decision-making that can ‘age out’ before the ink on the control chart dries.
Process intelligence changes that equation. Process Mining, Discrete Event Simulation, and real-time monitoring provide deep insights into how work really flows, and enables fast, effective decision-making. Outliers, rework loops, and bottlenecks surface in minutes or hours instead of weeks, giving Lean Six Sigma teams the live evidence they need to target and verify improvements.
Think of process intelligence as the telemetry layer that keeps DMAIC moving at the speed of the business. Where LSS asks “How does the process perform?”, process intelligence answers in real time, with statistical rigor and without clipboard bias.
What is Lean Six Sigma Today?
Lean Six Sigma (LSS) still revolves around the DMAIC cycle:
| Phase | Core Question | Common Deliverables |
| Define | What problem matters to customers? (If Lean analysis suggests a solution, stop. Try the fix.) | CTQ statements, project charter |
| Measure | How does the process really perform? | Baseline metrics, capability analysis |
| Analyze | Why is the variation happening? | Root-cause analysis / diagram, hypothesis test |
| Improve | What fixes will remove waste and defects? | Pilot changes, cost-benefit model, DOE |
| Control | How do we keep the gains? | Control plan, monitoring dashboard |
Modern data challenges often slow the cycle down: manual time studies, siloed transaction logs, missing timestamps, and thousands of unseen process variants. As organizations mature, those gaps widen—digital transactions multiply, regulatory audits tighten, and customers expect near-instant results.
That’s why mature LSS programs desire faster, automated insight. They need live process metrics (not quarterly samples) to spot drift, validate fixes, and prove compliance without launching another clipboard-heavy study. Pairing DMAIC with process-intelligence solutions delivers that speed, turning Lean Six Sigma from a project-based exercise into an always-on operational discipline.
What Is Process Intelligence?
Process intelligence stitches together four complementary capabilities—process mining, task mining, discrete event simulation, and continuous monitoring—to deliver a living, breathing picture of operations:
- Process mining extracts time-stamped events from core systems (ERP, CRM, HR) to auto-generate an end-to-end process, and provides tools analyze that process.
- Task mining captures user-level actions (keystrokes, screens) that fill the gaps between system events, revealing true hand-offs and manual workarounds.
- Simulation lets teams test “what-if” scenarios in a risk-free sandbox, forecasting cycle-time, cost, and capacity impacts before committing real resources. It allows virtual Design of Experiments (DOE); particularly where it would be too expensive, slow, or otherwise impractical to run.
- Monitoring keeps a live watch on key metrics, flagging deviations the moment a process drifts out of spec. With Predictive Analysis, you also can flag issues before they occur.
Together, these disciplines create an X-ray of your “as-is” execution. Every loop, delay, and compliance exception become visible—and quantifiable—in near real time. That clarity is what allows continuous-improvement teams to move from periodic diagnostics to continuous optimization.
Where Lean Six Sigma & Process Intelligence Converge
When closely examined, it becomes obvious that LSS and process intelligence can be naturally complementary too each other.
| Lean Six Sigma Need | Process Intelligence Capability | Resulting Advantage |
| Data collection (“Measure/Analyze/Improve”) | Automated event log ingestion | Weeks → minutes or hours |
| Root-cause analysis (“Analyze”) | Variant comparison, conformance checking, waiting statistics | Pinpoint bottlenecks instantly |
| Future-state validation (“Improve”) | Mining, Simulation (including DOE) & digital twins | Test and validate changes risk-free |
| Control chart monitoring (“Control”) | Live KPIs & alerts | Sustain gains, spot drift |
This combined approach can have measurable benefits for organizations:
- Significantly faster DMAIC Cycles
- Up-to-date Process Maps (eliminate static Visio files)
- Data-driven Project Selection (rank by ROI, compliance risk)
- Reduced Rework & Defects (real-time detection)
- Audit-Ready Evidence (traceable logs, version control)
- Foundation for Agentic AI & Automation
Three High-Impact Use Cases
There are countless scenarios—across industries and business functions—where combining Lean Six Sigma discipline with process-intelligence insight delivers meaningful gains. Here are three examples:
Loan-Origination Cycle Time (Banking & Financial Services)
A bank’s continuous-improvement team suspects that excessive rework is slowing approvals but lacks the hard data to prove it. Process intelligence reveals clusters of little-known process variants and pinpoints exactly where redundant approvals occur. By simulating a streamlined path, the bank can see how trimming even one step would accelerate funding and capture more interest revenue—turning customer frustration into a competitive edge.
Claims Adjudication Accuracy (Insurance)
Rising audit findings suggest hidden process defects, yet root causes remain fuzzy through traditional analysis alone. Real-time anomaly detection highlights claims that deviate from the most efficient route and triggers immediate interventions. Lean Six Sigma tools then refine hand-offs and error controls. The result is a significant boost in first-pass accuracy, fewer regulatory headaches, and a clearer compliance trail.
Patient Journey (Healthcare)
After a DMAIC project exposes bottlenecks in wait times, patients leaving without treatment are impacting a hospital system’s revenue. Process simulation highlights specific changes in staffing, scheduling and triage processes that will optimize the patient journey. This results in a higher volume of patients seen, increased satisfaction with the experience, and more revenue for the hospital.
Across all three cases, the pattern is the same: Lean Six Sigma frames the problem and structures the fix; process intelligence provides tools to analyze and improve the process, and supplies the continuous, system-level evidence that keeps improvements on track.
Integrating Process Intelligence into Lean Six Sigma
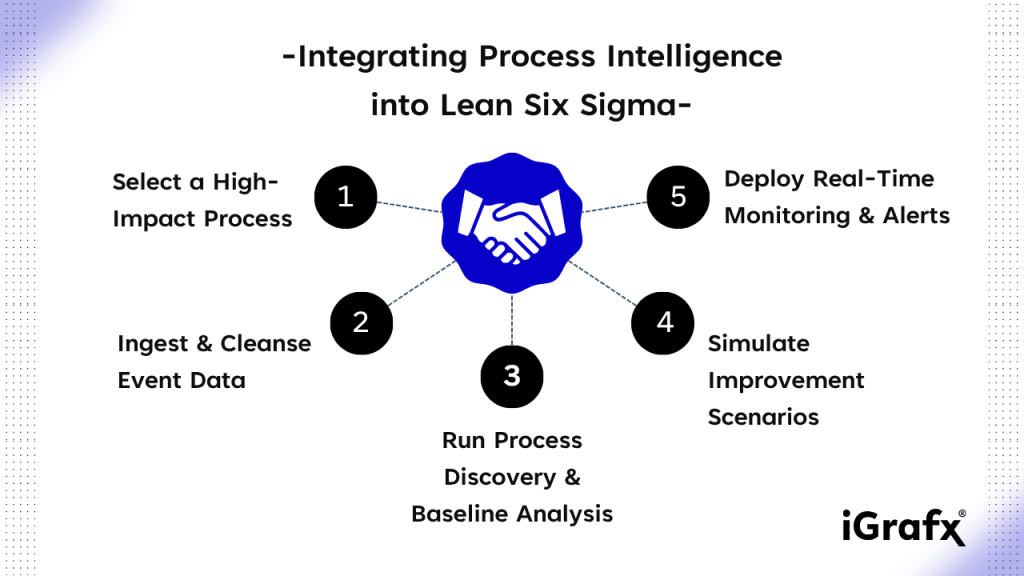
Let’s examine a 5-step roadmap to achieving success with your new dynamic duo:
- Select a High-Impact Process
Start with an area that visibly affects margin, customer experience, or compliance—order-to-cash, claims adjudication, or sterile-device turnaround are classic candidates. Confirm it has sufficient volume and stakeholder buy-in so early wins can scale across the enterprise. - Ingest & Cleanse Event Data
Pull time-stamped logs from ERP, CRM, MES, and other core systems, then standardize case IDs, timestamps, and activity names. A quick data-quality pass—de-duplication, outlier handling, and missing-field checks—prevents noise from skewing downstream analysis. - Run Process Discovery & Baseline Analysis
Use process and task mining to auto-generate the “as-is” flow, exposing hidden variants, loops, and rework. Quantify waste in cycle time, touch time, and defect cost so Lean Six Sigma teams have hard numbers to feed into their DMAIC Measure and Analyze phases. - Simulate Improvement Scenarios
Model proposed fixes—parallel approvals, automation hand-offs, new control points—and test them against DMAIC hypotheses. Simulation predicts the impact on throughput, cost, and risk before a single change touches production, de-risking the Improve phase. - Deploy Real-Time Monitoring & Alerts
Embed dashboards and statistical alarms that watch key KPIs 24/7, closing the Control loop. When a metric drifts outside limits—say, first-pass-yield drops or wait time spikes—the system flags it instantly so owners can intervene before small deviations become systemic defects.
Spotlight on iGrafx Process360 Live: The Process Intelligence Platform
iGrafx integrates process mining, modeling, simulation, and predictive analytics into a single platform, eliminating the swivel-chair work that often derails improvement projects. Three pillars keep teams aligned:
- Discover—Mine event data to reveal the “as-is” process with 100 % transparency, including parallel flows and hidden handoffs.
- Design—Model future-state scenarios, inject risk controls, and test changes in a sandbox before rollout.
- Optimize—Apply AI-driven monitoring that flags deviations, predicts capacity issues, .
Because the platform stores models, simulations, procedures, and risk controls in a centralized repository, Black Belts and business owners always work from the same source of truth—a major boost for collaboration and compliance.
Contact iGrafx today to learn more about the power duo of Lean Six Sigma and process intelligence and how it could help your organization.